You've poured your heart into creating amazing content, optimized every headline, and built a few backlinks. But when you search for it on Google... nothing. It's a frustrating reality for many website owners, and the culprit is often simpler than you think: indexing issues.
If Google can't find, crawl, or understand your pages, they simply won't appear in search results. Your hard work remains invisible to the world.
The good news? Google Search Console (GSC) is your secret weapon for diagnosing these problems. In this post, we’ll break down 12 of the most common GSC indexing issues and provide simple, actionable steps you can take to fix them right away.
Let's dive in and get your pages the visibility they deserve.
1. Not Found (404 Error)
• What It Means: Google has found a URL that exists in your sitemap or through internal links, but when it tries to visit, your server returns a "page not found" error. This wastes your crawl budget and creates a poor user experience.
• How to Fix It:
o If the page has moved: Create a 301 redirect from the old, broken URL to the new, live URL.
o If the page is gone for good: Find and fix any broken internal links on your site that are pointing to the defunct URL.
.png)
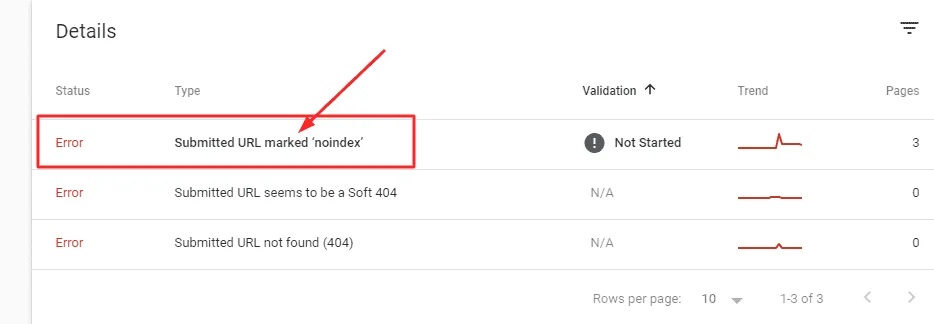
2. Submitted URL Marked with 'Noindex'
• What It Means: You've asked Google to index a page (by submitting it in GSC or via your sitemap), but the page contains a noindex meta tag that explicitly tells search engines not to index it. Google sees this contradiction and honors the noindex directive.
• How to Fix It:
o To get it indexed: Remove the noindex tag from the page's HTML
section or your CMS settings (like Yoast SEO or RankMath).
o If you don't want it indexed: Remove the page from your XML sitemap to stop submitting it for indexing.
3. Blocked by Robots.txt
• What It Means: Your robots.txt file contains a Disallow rule that is blocking Googlebot from crawling specific pages or resources. Since Google can't crawl it, it can't index it
• How to Fix It:
o Review your robots.txt file (found at yoursite.com/robots.txt) and remove the Disallow rule for any important pages you want indexed.
o Use the robots.txt Tester in Google Search Console to identify exactly which rules are blocking your pages.
.png)
4. Discovered - Currently Not Indexed
• What It Means: Google is aware of your page (it discovered it through a sitemap or links) but hasn't gotten around to crawling and indexing it yet. This is often a low-priority or crawl budget issue.
• How to Fix It:
o Increase its importance: Add strong, relevant internal links from your high-traffic, well-indexed pages to this undiscovered page.
o Improve signals: Ensure the page has high-quality, unique content to make it more appealing for Google to crawl.
.png)
5. Crawled - Currently Not Indexed
• What It Means: This is a more concerning status. Google crawled the page but made a conscious decision not to index it. This is typically due to quality issues, thin content, or it being a near-duplicate of another page.
• How to Fix It:
o Boost content quality: Significantly improve the page by adding more depth, originality, and valuable information. Aim for comprehensive coverage of the topic.
o Ensure uniqueness: Audit your site to make sure the page isn't a duplicate or too similar to other pages on your site.
.png)
6. Soft 404 Error
• What It Means: Your server returns a "200 OK" success status (meaning the page loaded technically), but the page itself is empty, has very little content, or looks like an error page. Google interprets this as a "soft" 404.
• How to Fix It:
o Add real content: Populate the page with valuable, relevant content that serves a purpose.
o Use a real redirect or 404: If the content is truly gone, replace the soft error with a proper 301 redirect to a relevant page or a hard 410 (Gone) status code.
.png)
7. Soft 404 Error
• What It Means: Your server was overloaded, under maintenance, or had a technical glitch when Googlebot came to visit. As a result, Google couldn't access the page.
• How to Fix It:
o Check server health: Contact your hosting provider to investigate server stability and uptime.
o Monitor logs: Check your server error logs for recurring 5xx errors and fix underlying database or configuration problems.
.png)
8. Page with Redirect
• What It Means: The specific URL you asked Google to index is actually just a redirect (e.g., a 301 or 302) to another page. Google indexes the final destination URL, not the redirecting URL.
• How to Fix It:
o Update internal links: Change all internal links on your site to point directly to the final, destination URL.
o Update your sitemap: Ensure your XML sitemap only contains final URLs, not URLs that redirect.
.png)
9. Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403):
• What It Means: Googlebot was blocked from accessing the page by your servers, which returned a "403 Forbidden" Status. The server understood the request but refused to fulfill it.
• How to Fix It:
o Check security settings: Reviews your robots.txt, . htaccess file, and any setting plugins (like Wordfence) for rules that might be blocking Googlbot.
o Whitelist Googlebot: Ensure your server firewall or security settings are not blocking Googlebot's IP ranges.
.png)
10. Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
• What It Means: Google has found multiple pages with very similar and identical content on your site. but you haven't specified which version is the "main" one (the canonical). This forces Google to Guess, and it might choose the wrong one.
• How to Fix It:
o Specify the original: Add a rel= "canonical" tag to all duplicate pages, pointing to the single URL you want to be indexed.
o Consolidate pages: For very similar pages, use a 301 redirect to merge them into a authoritative page.
.png)
11. Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag
• What It Means: This is often not an error! It menas you have correctly implemented a canonical tag on this page, pointing to another URL as the main version. Because It's an "alternate" page, Google is correctly not indexing it.
• How to Fix It:
o Specify the original: Add a rel= "canonical" tag to all duplicate pages, pointing to the single URL you want to be indexed.
o Consolidate pages: For very similar pages, use a 301 redirect to merge them into a authoritative page.
.png)
12. Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical Than User
• What It Means: You told Google which page is the main one via a canonical tag, but Google ignored your suggestion and chose a different page from the group as the canonocal. This happen when Google believes the other page is more relevant of of higher quality.
• How to Fix It:
o Improve your chosen page: Add more unique, valuable, and comprehensive contnet to the page you want to be canonical. Ensure it has a clear purpose and is linked to appropriately internally.
o Force the issues: The most robust solution is to use a 301 redirect from the less-preferred page to your chosen canonical URL, eliminating the duplicate altogether.
.png)
Get Indexed, Get Seen
Fixing indexing issues is one of the most impactful SEO tasks you can perform. It's the fundamental step that takes your content from sitting on your server to competing in the search results.
By regularly monitoring your Google Search Console coverage report and acting on these common issues, you can ensure Google can efficiently find, crawl, and index your best work. Now, open up GSC, run a diagnostic, and start fixing





